A Super Stadium
Downloads
- superbowl_oli_20250202_lrg.jpg (1472x981, JPEG)
Metadata
- Sensor(s):
- Landsat 8 - OLI
- Data Date: February 2, 2025
- Visualization Date: February 7, 2025
On February 9, 2025, the Kansas City Chiefs and Philadelphia Eagles will face off in New Orleans in Super Bowl LIX. This will be the 11th Super Bowl played in New Orleans, tying it with Miami for the most times a city has hosted the championship football game.
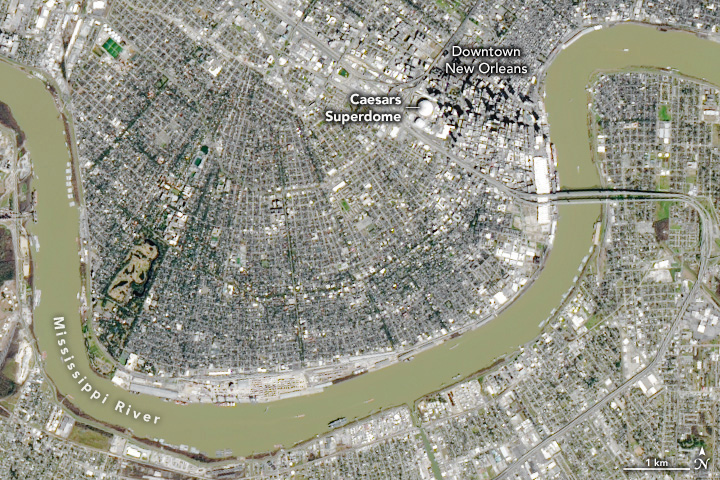
The game will take place in the Caesars Superdome, what the owners of the building describe as the largest fixed-dome structure in the world. The OLI (Operational Land Imager) on Landsat 8 captured this image of the stadium on February 2, 2025. The dark areas to the east of the Superdome are shadows cast by buildings in downtown New Orleans. The white roof is coated with spray polyurethane foam, an insulating and water-resistant material that is also used to insulate some NASA rocket engines.
For football games, the Superdome has a seating capacity of 74,295 people. Nearly 400,000 square feet of aluminum make up the structure’s exterior skin. The roof covers an area of 9.7 acres (3.9 hectares), making it the world’s largest entirely steel-constructed arena unobstructed by posts or columns. The roof was repaired in 2006 after being severely damaged by Hurricane Katrina.
Skies were clear when this image was captured, but forecasters warned that a mixture of smoke and low clouds called super fog would likely cover parts of the city in the days prior to the game, disrupting traffic and reducing visibility to less than 10 feet (3 meters). The dense fog forms when smoke and moisture released from damp, smoldering organic material mix with nearly saturated air, according to the National Weather Service. The smoke is coming from a large marsh fire burning southwest of the city, in St. Charles Parish.
On Super Bowl Sunday, temperatures are expected to be about 74 degrees Fahrenheit (23 degrees Celsius) in the climate-controlled Superdome. Forecasts indicate that outdoor temperatures will range from the mid-70s to 80s, about 10°F above normal for this time of year.
References
- Caesars Superdome (2015) 10 Years After Katrina. Accessed February 7, 2025.
- ESPN (2025, February 5) New Orleans among cities that have hosted most Super Bowls. Accessed February 7, 2025.
- Fox Weather (2025, February 6) Super fog could impact travel to Super Bowl in New Orleans. Accessed February 7, 2025.
- NASA Earthdata (2025, February 2) New Orleans and Lake Pontchartrain Before the Super Bowl. Accessed February 7, 2025.
- NASA (2025, January 27) NASA Invites Media to Pre-Super Bowl Tours at New Orleans Facility. Accessed February 7, 2025.
- NASA (2023, April 19) Technicians Apply Foam to Moon Rocket Hardware for Artemis III. Accessed February 7, 2025.
- NASA Landsat (2010, January 6) New Orleans. Accessed February 7, 2025.
- NASA Scientific Visualization Studio (2003, January 14) Great Zoom into New Orleans, LA: The Louisiana Superdome. Accessed February 7, 2025.
- National Weather Service Super Fog. Accessed February 7, 2025.
- ThoughtCo. (2019, July 3) How the Louisiana Superdome Saved Lives. Accessed February 7, 2025.
- Spray Foam Magazine (2020) Going Farther and Faster with Foam. Accessed February 7, 2025.
- The Weather Channel (2025, February 7) Super Bowl LIX Host City New Orleans Was The Site Of The Coldest Super Bowl Over 50 Years Ago. Accessed February 7, 2025.
- WWL-TV (2025, February 6) Large marsh fire burning in St. Charles Parish, super fog possible overnight. Accessed February 7, 2025.
- Yahoo Sports (2025, February 3) Super Bowl 2025: Why the Superdome is America’s greatest sports venue. Accessed February 7, 2025.
NASA Earth Observatory image by Wanmei Liang, using Landsat data from the U.S. Geological Survey. Story by Adam Voiland.
This image record originally appeared on the Earth Observatory. Click here to view the full, original record.