Gold Mining in Russia’s Central Aldan Ore District
Downloads
- aldan_oli_2019245_lrg.jpg (5442x4430, JPEG)
- aldanmine_oli_2019245.jpg (720x480, JPEG)
- aldandredging_oli_2019245.jpg (720x480, JPEG)
Metadata
- Sensor(s):
- Landsat 8 - OLI
- Data Date: September 11, 2019
- Visualization Date: January 29, 2021
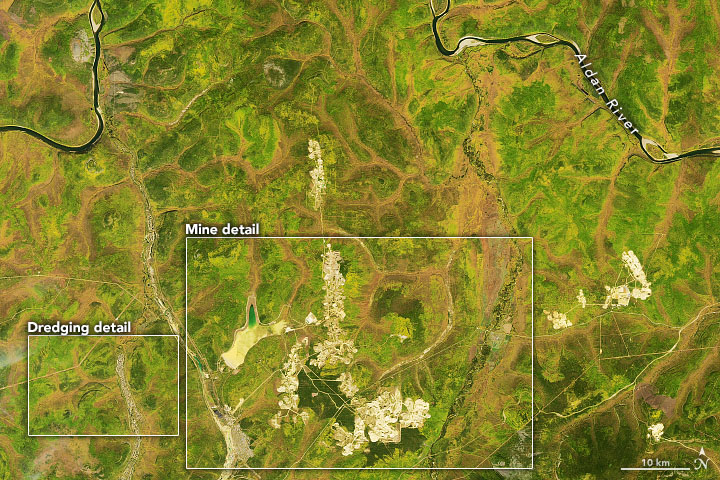
Gold has been found on every continent except Antarctica, but the lustrous yellow metal is not exactly ubiquitous. The element (Au on the periodic table) is actually quite rare, accounting for just one out of every billion atoms in Earth’s crust. But in places such as the Central Aldan ore district in the Russian Far East—where concentrations of the precious metal have been discovered—mining operations are large enough to be seen from space.
On September 11, 2019, the Operational Land Imager (OLI) on Landsat 8 acquired this natural-color image showing part of the ore district in the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia). The image is centered about 25 kilometers (15 miles) northwest of the gold-mining town of Aldan, and about 450 kilometers southwest of the regional capital city, Yakutsk.
Central Aldan is one of Russia’s largest gold ore districts, with the mineral occurring in numerous deposits, or “lodes,” in the fractured rock. One of the largest lodes lies in the Kuranakh deposit, a shallow, ribbon-like orebody (up to 50 meters thick and 25 kilometers long) sandwiched between Cambrian limestone below and Jurassic sandstone above. A mining site developed to to extract this gold is visible in the detailed image below.
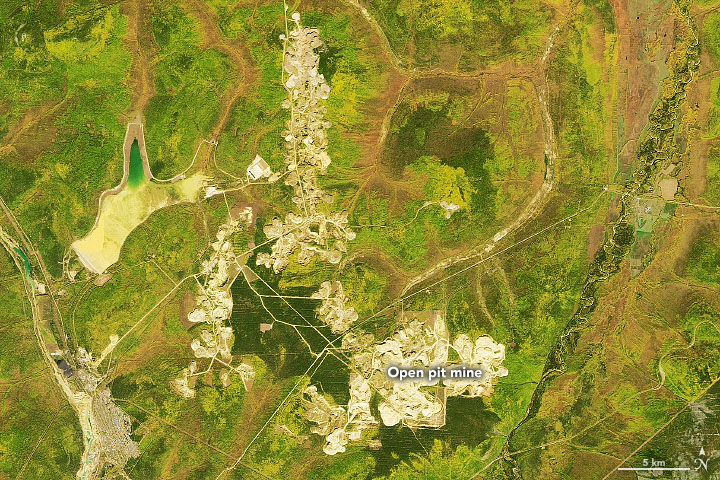
The Kuranakh gold deposit was discovered in 1947, and a moderate amount of gold was extracted by 1955. Ten years later, large-scale open-pit mining began and continues today. Open-cut, drilling, and blasting techniques are now used to access the ore, which is processed at an onsite mill. In 2019, the Kuranakh mine produced 224,700 ounces of refined gold.
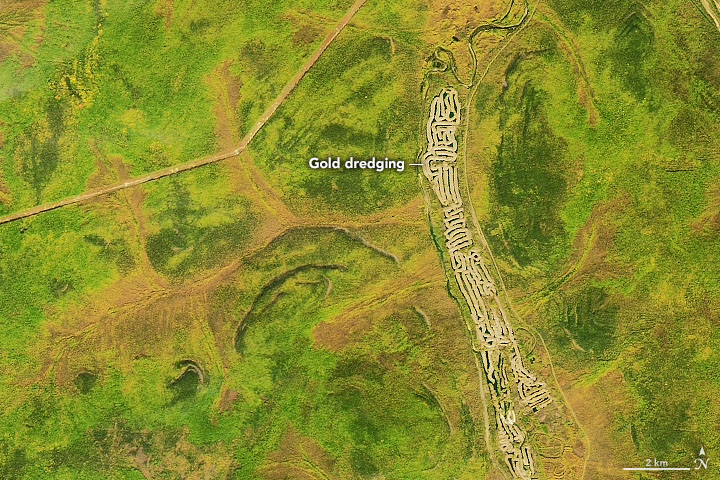
Not all of the region’s gold shows up as lode deposits. In areas where a lode has been eroded, pieces of gold can become concentrated by rivers and streams into placer deposits. The second image, centered west of the town of Nizhny Kuranakh, shows the excavation site of buried placer along a tributary of the Aldan River.
To excavate the placer, bucket-lined dredges scoop up material in the front and dump the tailings behind in curved piles. The accumulation of arc-shaped piles forms the long, maze like-pattern, which is visible in the image above. From April to December in the 2019 mining season, three dredges extracted 18,600 ounces of gold from the Bolshoy Kuranakh placer deposit.
References
- American Museum of Natural History World Gold Deposits. Accessed January 29, 2021. is
- Gorryachev, N. A. and Pirajno, F. (2014) Gold deposits and gold metallogeny of Far East Russia. Ore Geology Reviews, 59 (2014), 123–151.
- Grayson, R. (2010) Large gold dredges—impacts in USA, Canada, Russia, Mongolia and China. World Placer Journal 10, 1–20.
- GV Gold (2021, January 27) Aldan Business Unit. Accessed January 29, 2021.
- NASA JPL, ASTER (2020, September 21) Aldan, Siberia, Russia. Accessed January 29, 2021.
- Polyus Kuranakh. Accessed January 29, 2021.
- Rodionov, S. M. et al. (2005) The Kuranakh epithermal gold deposit, East Russia. Mineral Deposit Research: Meeting the Global Challenge, 1053–1056.
NASA Earth Observatory images by Joshua Stevens, using Landsat data from the U.S. Geological Survey. Story by Kathryn Hansen.
This image record originally appeared on the Earth Observatory. Click here to view the full, original record.